Information
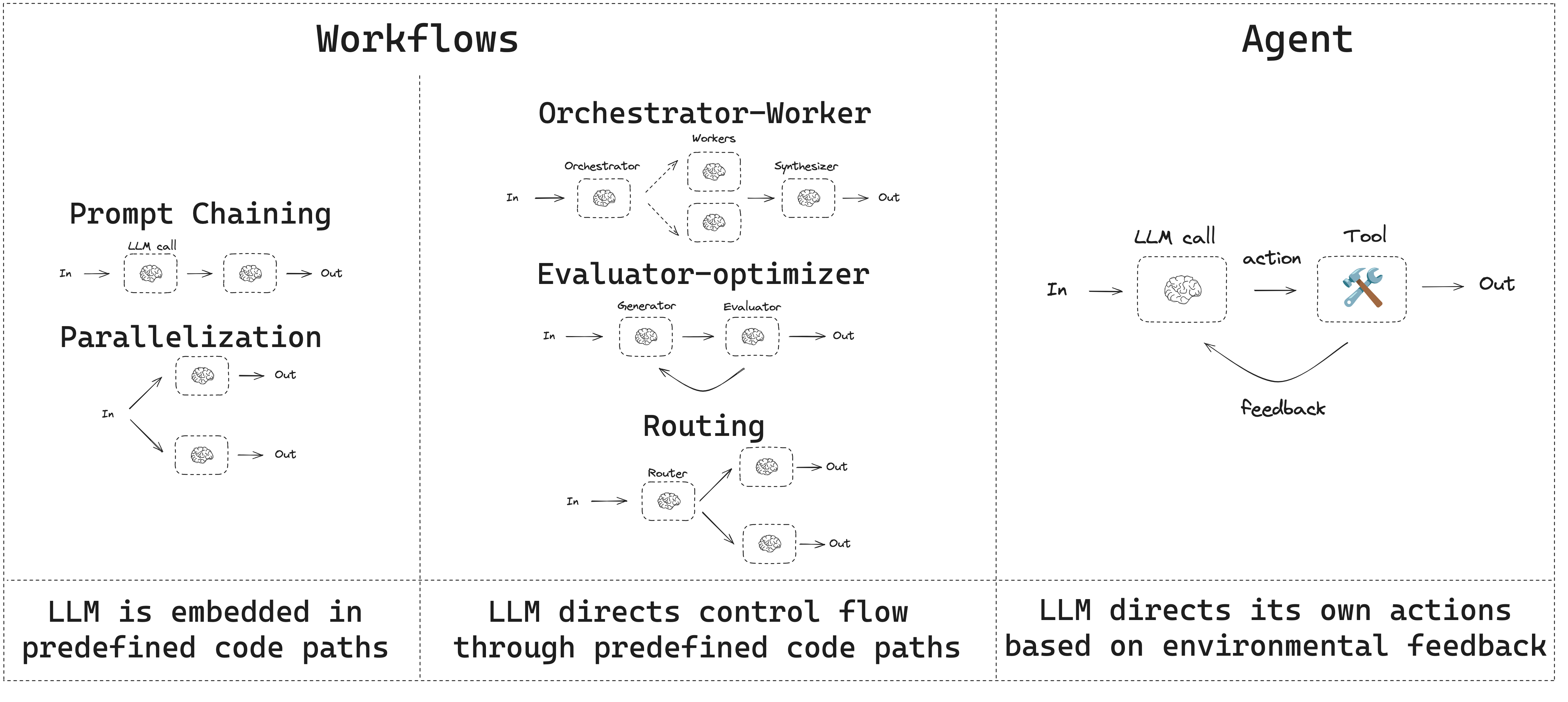
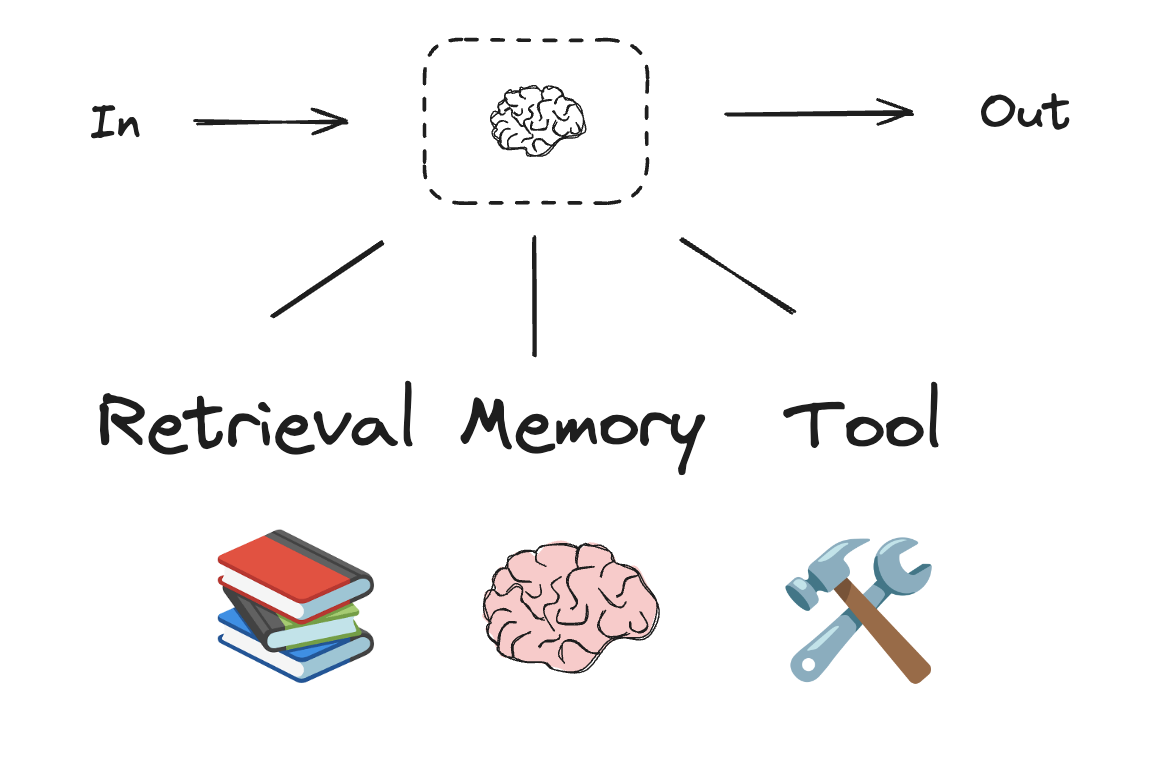
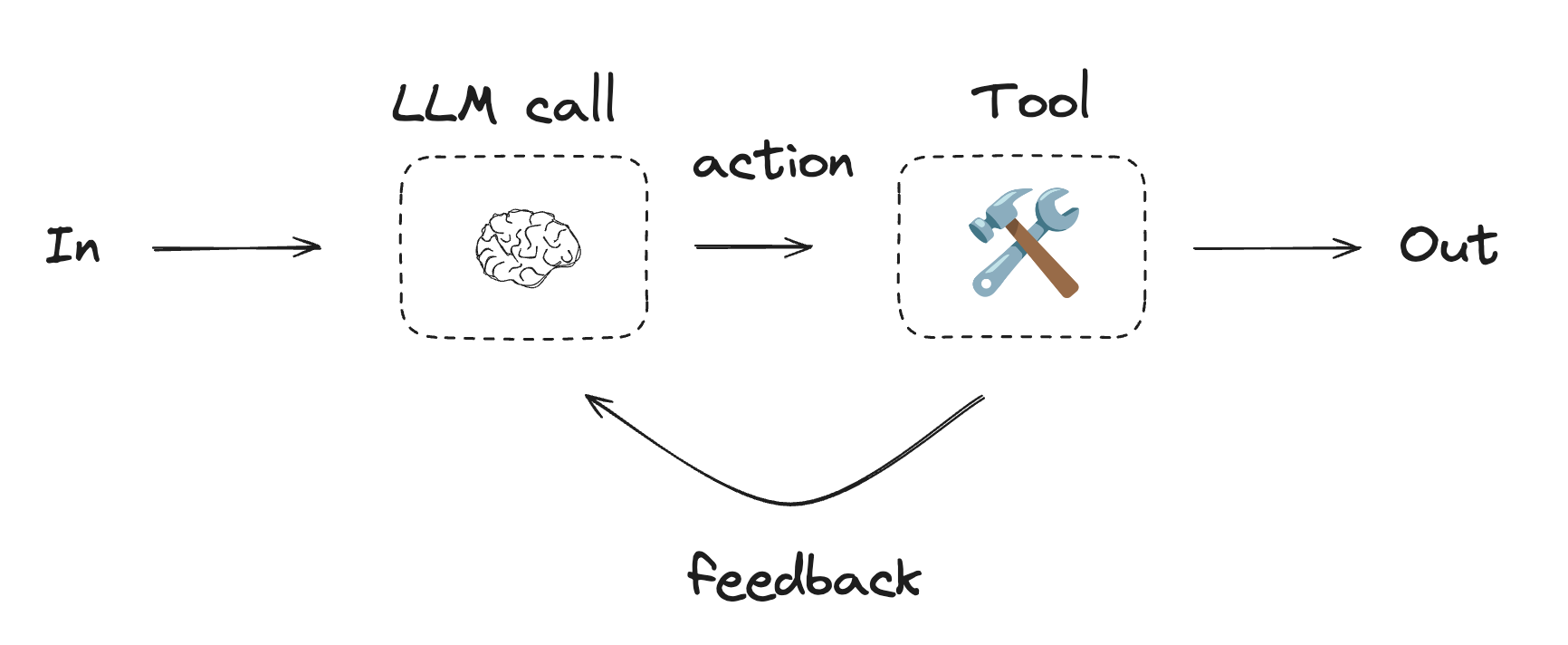
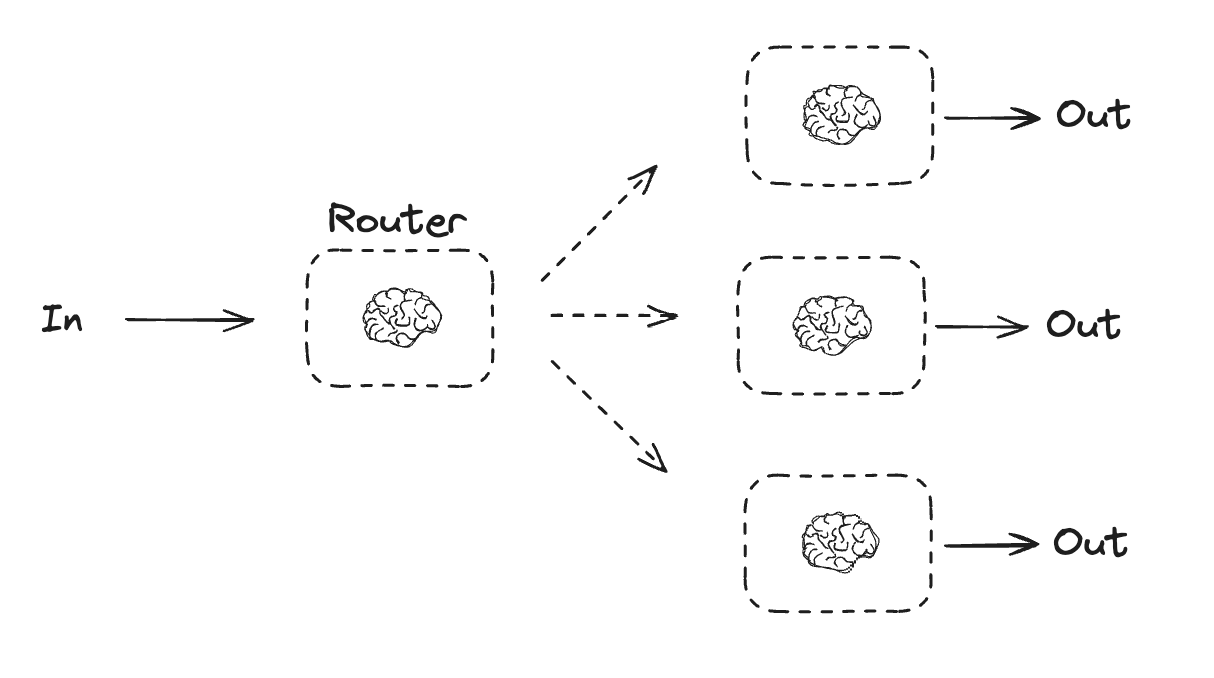
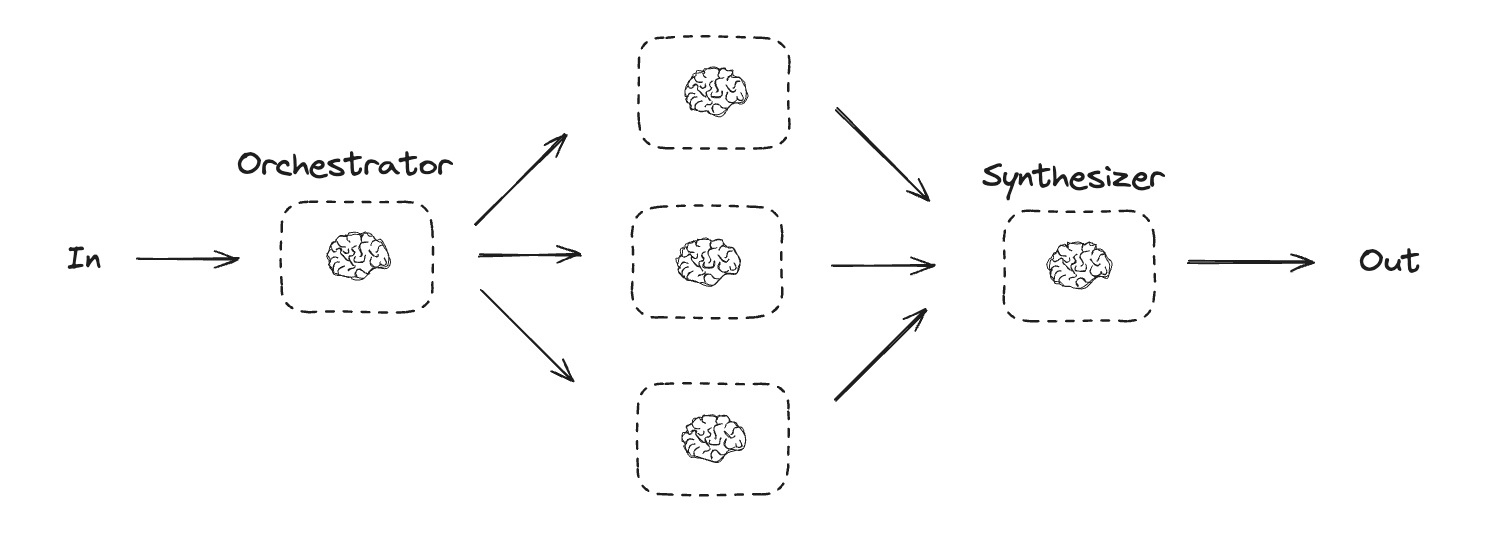
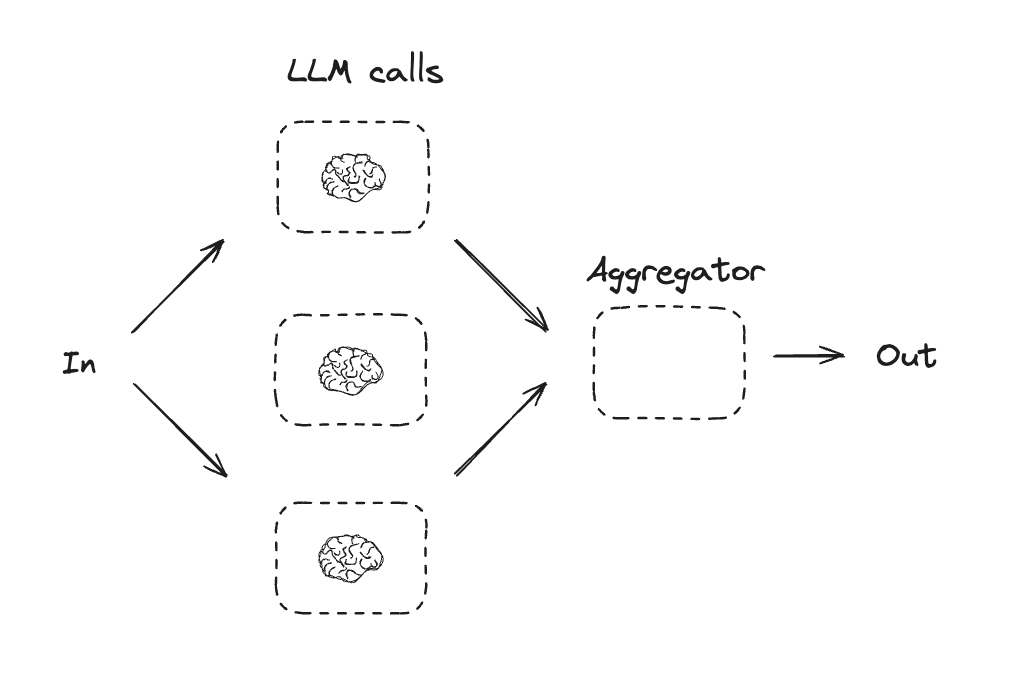
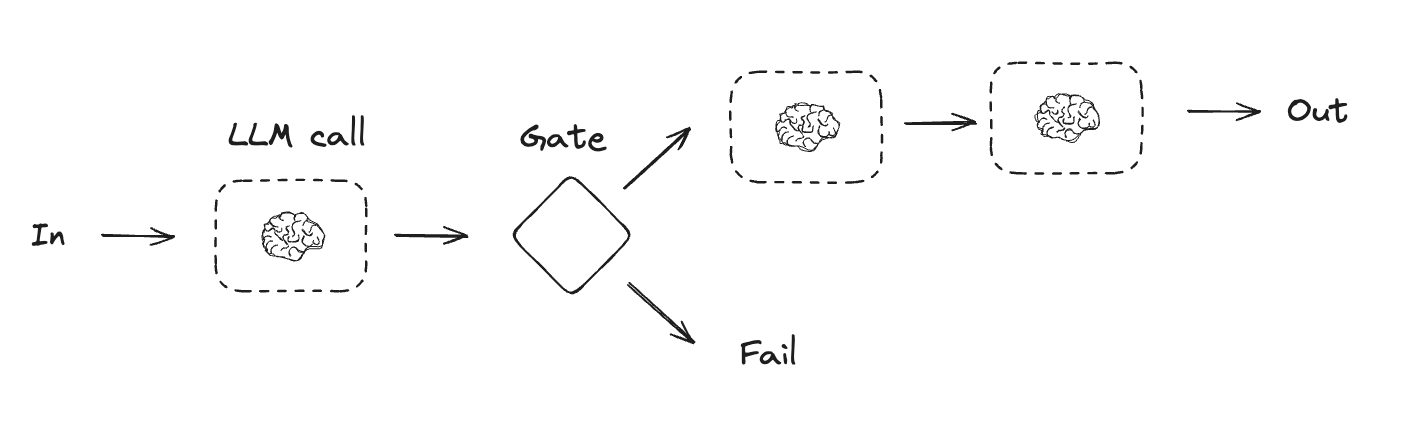
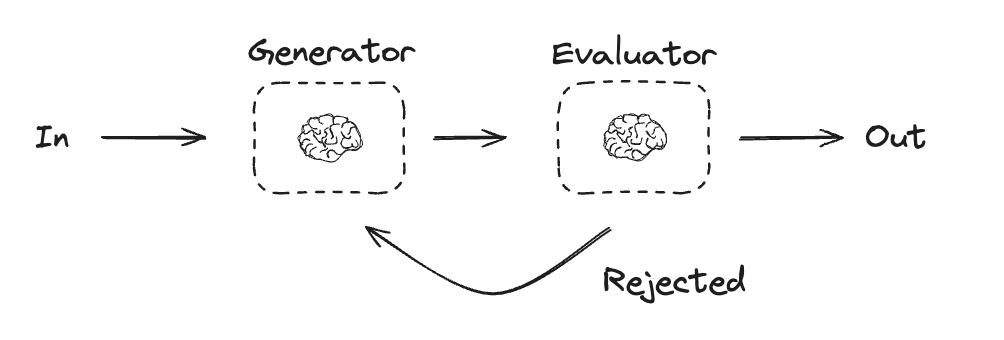
Workflows and Agents Home Get started Learn the basics Deployment Guides How-to Guides Concepts Tutorials Quick Start Quick Start Learn the basics Local Deploy Cloud Deploy Chatbots RAG Agent Architectures Evaluation & Analysis Experimental LangGraph Platform Resources Prebuilt Agents Companies using LangGraph FAQ Troubleshooting LangGraph Academy Course API reference Set up Building Blocks: The Augmented LLM Prompt chaining Parallelization Routing Orchestrator-Worker Evaluator-optimizer Agent Pre-built What LangGraph provides Persistence: Human-in-the-Loop Persistence: Memory Streaming Deployment Home Guides Tutorials Quick Start pip install langchain_core langchain-anthropic langgraph import os import os import getpass import getpass from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic def _set_env(var: str): def _set_env ( var : str ): if not os.environ.get(var): if not os . environ . get ( var ): os.environ[var] = getpass.getpass(f"{var}: ") os . environ [ var ] = getpass . getpass ( f " { var } : " ) _set_env("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY") _set_env ( "ANTHROPIC_API_KEY" ) llm = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-latest") llm = ChatAnthropic ( model = "claude-3-5-sonnet-latest" ) # Schema for structured output # Schema for structured output from pydantic import BaseModel, Field from pydantic import BaseModel , Field class SearchQuery(BaseModel): class SearchQuery ( BaseModel ): search_query: str = Field(None, description="Query that is optimized web search.") search_query : str = Field ( None , description = "Query that is optimized web search." ) justification: str = Field( justification : str = Field ( None, description="Why this query is relevant to the user's request." None , description = "Why this query is relevant to the user's request." ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(SearchQuery) structured_llm = llm . with_structured_output ( SearchQuery ) # Invoke the augmented LLM # Invoke the augmented LLM output = structured_llm.invoke("How does Calcium CT score relate to high cholesterol?") output = structured_llm . invoke ( "How does Calcium CT score relate to high cholesterol?" ) # Define a tool # Define a tool def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int: def multiply ( a : int , b : int ) -> int : return a * b return a * b # Augment the LLM with tools # Augment the LLM with tools llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([multiply]) llm_with_tools = llm . bind_tools ([ multiply ]) # Invoke the LLM with input that triggers the tool call # Invoke the LLM with input that triggers the tool call msg = llm_with_tools.invoke("What is 2 times 3?") msg = llm_with_tools . invoke ( "What is 2 times 3?" ) # Get the tool call # Get the tool call msg.tool_calls msg . tool_calls from typing_extensions import TypedDict from typing_extensions import TypedDict from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END from langgraph.graph import StateGraph , START , END from IPython.display import Image, display from IPython.display import Image , display # Graph state # Graph state class State(TypedDict): class State ( TypedDict ): topic: str topic : str joke: str joke : str improved_joke: str improved_joke : str final_joke: str final_joke : str # Nodes # Nodes def generate_joke(state: State): def generate_joke ( state : State ): """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a short joke about {state['topic']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a short joke about { state [ 'topic' ] } " ) return {"joke": msg.content} return { "joke" : msg . content } def check_punchline(state: State): def check_punchline ( state : State ): """Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline""" """Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline""" # Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!" # Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!" if "?" in state["joke"] or "!" in state["joke"]: if "?" in state [ "joke" ] or "!" in state [ "joke" ]: return "Fail" return "Fail" return "Pass" return "Pass" def improve_joke(state: State): def improve_joke ( state : State ): """Second LLM call to improve the joke""" """Second LLM call to improve the joke""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: {state['joke']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: { state [ 'joke' ] } " ) return {"improved_joke": msg.content} return { "improved_joke" : msg . content } def polish_joke(state: State): def polish_joke ( state : State ): """Third LLM call for final polish""" """Third LLM call for final polish""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Add a surprising twist to this joke: {state['improved_joke']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Add a surprising twist to this joke: { state [ 'improved_joke' ] } " ) return {"final_joke": msg.content} return { "final_joke" : msg . content } # Build workflow # Build workflow workflow = StateGraph(State) workflow = StateGraph ( State ) # Add nodes # Add nodes workflow.add_node("generate_joke", generate_joke) workflow . add_node ( "generate_joke" , generate_joke ) workflow.add_node("improve_joke", improve_joke) workflow . add_node ( "improve_joke" , improve_joke ) workflow.add_node("polish_joke", polish_joke) workflow . add_node ( "polish_joke" , polish_joke ) # Add edges to connect nodes # Add edges to connect nodes workflow.add_edge(START, "generate_joke") workflow . add_edge ( START , "generate_joke" ) workflow.add_conditional_edges( workflow . add_conditional_edges ( "generate_joke", check_punchline, {"Fail": "improve_joke", "Pass": END} "generate_joke" , check_punchline , { "Fail" : "improve_joke" , "Pass" : END } ) ) workflow.add_edge("improve_joke", "polish_joke") workflow . add_edge ( "improve_joke" , "polish_joke" ) workflow.add_edge("polish_joke", END) workflow . add_edge ( "polish_joke" , END ) # Compile # Compile chain = workflow.compile() chain = workflow . compile () # Show workflow # Show workflow display(Image(chain.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( chain . get_graph () . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke state = chain.invoke({"topic": "cats"}) state = chain . invoke ({ "topic" : "cats" }) print("Initial joke:") print ( "Initial joke:" ) print(state["joke"]) print ( state [ "joke" ]) print("\n--- --- ---\n") print ( " \n --- --- --- \n " ) if "improved_joke" in state: if "improved_joke" in state : print("Improved joke:") print ( "Improved joke:" ) print(state["improved_joke"]) print ( state [ "improved_joke" ]) print("\n--- --- ---\n") print ( " \n --- --- --- \n " ) print("Final joke:") print ( "Final joke:" ) print(state["final_joke"]) print ( state [ "final_joke" ]) else: else : print("Joke failed quality gate - no punchline detected!") print ( "Joke failed quality gate - no punchline detected!" ) from langgraph.func import entrypoint, task from langgraph.func import entrypoint , task # Tasks # Tasks @task @task def generate_joke(topic: str): def generate_joke ( topic : str ): """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a short joke about {topic}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a short joke about { topic } " ) return msg.content return msg . content def check_punchline(joke: str): def check_punchline ( joke : str ): """Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline""" """Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline""" # Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!" # Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!" if "?" in joke or "!" in joke: if "?" in joke or "!" in joke : return "Fail" return "Fail" return "Pass" return "Pass" @task @task def improve_joke(joke: str): def improve_joke ( joke : str ): """Second LLM call to improve the joke""" """Second LLM call to improve the joke""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: {joke}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: { joke } " ) return msg.content return msg . content @task @task def polish_joke(joke: str): def polish_joke ( joke : str ): """Third LLM call for final polish""" """Third LLM call for final polish""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Add a surprising twist to this joke: {joke}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Add a surprising twist to this joke: { joke } " ) return msg.content return msg . content @entrypoint() @entrypoint () def parallel_workflow(topic: str): def parallel_workflow ( topic : str ): original_joke = generate_joke(topic).result() original_joke = generate_joke ( topic ) . result () if check_punchline(original_joke) == "Pass": if check_punchline ( original_joke ) == "Pass" : return original_joke return original_joke improved_joke = improve_joke(original_joke).result() improved_joke = improve_joke ( original_joke ) . result () return polish_joke(improved_joke).result() return polish_joke ( improved_joke ) . result () # Invoke # Invoke for step in parallel_workflow.stream("cats", stream_mode="updates"): for step in parallel_workflow . stream ( "cats" , stream_mode = "updates" ): print(step) print ( step ) print("\n") print ( " \n " ) # Graph state # Graph state class State(TypedDict): class State ( TypedDict ): topic: str topic : str joke: str joke : str story: str story : str poem: str poem : str combined_output: str combined_output : str # Nodes # Nodes def call_llm_1(state: State): def call_llm_1 ( state : State ): """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {state['topic']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a joke about { state [ 'topic' ] } " ) return {"joke": msg.content} return { "joke" : msg . content } def call_llm_2(state: State): def call_llm_2 ( state : State ): """Second LLM call to generate story""" """Second LLM call to generate story""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a story about {state['topic']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a story about { state [ 'topic' ] } " ) return {"story": msg.content} return { "story" : msg . content } def call_llm_3(state: State): def call_llm_3 ( state : State ): """Third LLM call to generate poem""" """Third LLM call to generate poem""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a poem about {state['topic']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a poem about { state [ 'topic' ] } " ) return {"poem": msg.content} return { "poem" : msg . content } def aggregator(state: State): def aggregator ( state : State ): """Combine the joke and story into a single output""" """Combine the joke and story into a single output""" combined = f"Here's a story, joke, and poem about {state['topic']}!\n\n" combined = f "Here's a story, joke, and poem about { state [ 'topic' ] } ! \n\n " combined += f"STORY:\n{state['story']}\n\n" combined += f "STORY: \n { state [ 'story' ] } \n\n " combined += f"JOKE:\n{state['joke']}\n\n" combined += f "JOKE: \n { state [ 'joke' ] } \n\n " combined += f"POEM:\n{state['poem']}" combined += f "POEM: \n { state [ 'poem' ] } " return {"combined_output": combined} return { "combined_output" : combined } # Build workflow # Build workflow parallel_builder = StateGraph(State) parallel_builder = StateGraph ( State ) # Add nodes # Add nodes parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_1", call_llm_1) parallel_builder . add_node ( "call_llm_1" , call_llm_1 ) parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_2", call_llm_2) parallel_builder . add_node ( "call_llm_2" , call_llm_2 ) parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_3", call_llm_3) parallel_builder . add_node ( "call_llm_3" , call_llm_3 ) parallel_builder.add_node("aggregator", aggregator) parallel_builder . add_node ( "aggregator" , aggregator ) # Add edges to connect nodes # Add edges to connect nodes parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_1") parallel_builder . add_edge ( START , "call_llm_1" ) parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_2") parallel_builder . add_edge ( START , "call_llm_2" ) parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_3") parallel_builder . add_edge ( START , "call_llm_3" ) parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_1", "aggregator") parallel_builder . add_edge ( "call_llm_1" , "aggregator" ) parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_2", "aggregator") parallel_builder . add_edge ( "call_llm_2" , "aggregator" ) parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_3", "aggregator") parallel_builder . add_edge ( "call_llm_3" , "aggregator" ) parallel_builder.add_edge("aggregator", END) parallel_builder . add_edge ( "aggregator" , END ) parallel_workflow = parallel_builder.compile() parallel_workflow = parallel_builder . compile () # Show workflow # Show workflow display(Image(parallel_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( parallel_workflow . get_graph () . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke state = parallel_workflow.invoke({"topic": "cats"}) state = parallel_workflow . invoke ({ "topic" : "cats" }) print(state["combined_output"]) print ( state [ "combined_output" ]) @task @task def call_llm_1(topic: str): def call_llm_1 ( topic : str ): """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" """First LLM call to generate initial joke""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {topic}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a joke about { topic } " ) return msg.content return msg . content @task @task def call_llm_2(topic: str): def call_llm_2 ( topic : str ): """Second LLM call to generate story""" """Second LLM call to generate story""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a story about {topic}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a story about { topic } " ) return msg.content return msg . content @task @task def call_llm_3(topic): def call_llm_3 ( topic ): """Third LLM call to generate poem""" """Third LLM call to generate poem""" msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a poem about {topic}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a poem about { topic } " ) return msg.content return msg . content @task @task def aggregator(topic, joke, story, poem): def aggregator ( topic , joke , story , poem ): """Combine the joke and story into a single output""" """Combine the joke and story into a single output""" combined = f"Here's a story, joke, and poem about {topic}!\n\n" combined = f "Here's a story, joke, and poem about { topic } ! \n\n " combined += f"STORY:\n{story}\n\n" combined += f "STORY: \n { story } \n\n " combined += f"JOKE:\n{joke}\n\n" combined += f "JOKE: \n { joke } \n\n " combined += f"POEM:\n{poem}" combined += f "POEM: \n { poem } " return combined return combined # Build workflow # Build workflow @entrypoint() @entrypoint () def parallel_workflow(topic: str): def parallel_workflow ( topic : str ): joke_fut = call_llm_1(topic) joke_fut = call_llm_1 ( topic ) story_fut = call_llm_2(topic) story_fut = call_llm_2 ( topic ) poem_fut = call_llm_3(topic) poem_fut = call_llm_3 ( topic ) return aggregator( return aggregator ( topic, joke_fut.result(), story_fut.result(), poem_fut.result() topic , joke_fut . result (), story_fut . result (), poem_fut . result () ).result() ) . result () # Invoke # Invoke for step in parallel_workflow.stream("cats", stream_mode="updates"): for step in parallel_workflow . stream ( "cats" , stream_mode = "updates" ): print(step) print ( step ) print("\n") print ( " \n " ) from typing_extensions import Literal from typing_extensions import Literal from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage , SystemMessage # Schema for structured output to use as routing logic # Schema for structured output to use as routing logic class Route(BaseModel): class Route ( BaseModel ): step: Literal["poem", "story", "joke"] = Field( step : Literal [ "poem" , "story" , "joke" ] = Field ( None, description="The next step in the routing process" None , description = "The next step in the routing process" ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output router = llm.with_structured_output(Route) router = llm . with_structured_output ( Route ) # State # State class State(TypedDict): class State ( TypedDict ): input: str input : str decision: str decision : str output: str output : str # Nodes # Nodes def llm_call_1(state: State): def llm_call_1 ( state : State ): """Write a story""" """Write a story""" result = llm.invoke(state["input"]) result = llm . invoke ( state [ "input" ]) return {"output": result.content} return { "output" : result . content } def llm_call_2(state: State): def llm_call_2 ( state : State ): """Write a joke""" """Write a joke""" result = llm.invoke(state["input"]) result = llm . invoke ( state [ "input" ]) return {"output": result.content} return { "output" : result . content } def llm_call_3(state: State): def llm_call_3 ( state : State ): """Write a poem""" """Write a poem""" result = llm.invoke(state["input"]) result = llm . invoke ( state [ "input" ]) return {"output": result.content} return { "output" : result . content } def llm_call_router(state: State): def llm_call_router ( state : State ): """Route the input to the appropriate node""" """Route the input to the appropriate node""" # Run the augmented LLM with structured output to serve as routing logic # Run the augmented LLM with structured output to serve as routing logic decision = router.invoke( decision = router . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage( SystemMessage ( content="Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request." content = "Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request." ), ), HumanMessage(content=state["input"]), HumanMessage ( content = state [ "input" ]), ] ] ) ) return {"decision": decision.step} return { "decision" : decision . step } # Conditional edge function to route to the appropriate node # Conditional edge function to route to the appropriate node def route_decision(state: State): def route_decision ( state : State ): # Return the node name you want to visit next # Return the node name you want to visit next if state["decision"] == "story": if state [ "decision" ] == "story" : return "llm_call_1" return "llm_call_1" elif state["decision"] == "joke": elif state [ "decision" ] == "joke" : return "llm_call_2" return "llm_call_2" elif state["decision"] == "poem": elif state [ "decision" ] == "poem" : return "llm_call_3" return "llm_call_3" # Build workflow # Build workflow router_builder = StateGraph(State) router_builder = StateGraph ( State ) # Add nodes # Add nodes router_builder.add_node("llm_call_1", llm_call_1) router_builder . add_node ( "llm_call_1" , llm_call_1 ) router_builder.add_node("llm_call_2", llm_call_2) router_builder . add_node ( "llm_call_2" , llm_call_2 ) router_builder.add_node("llm_call_3", llm_call_3) router_builder . add_node ( "llm_call_3" , llm_call_3 ) router_builder.add_node("llm_call_router", llm_call_router) router_builder . add_node ( "llm_call_router" , llm_call_router ) # Add edges to connect nodes # Add edges to connect nodes router_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call_router") router_builder . add_edge ( START , "llm_call_router" ) router_builder.add_conditional_edges( router_builder . add_conditional_edges ( "llm_call_router", "llm_call_router" , route_decision, route_decision , { # Name returned by route_decision : Name of next node to visit { # Name returned by route_decision : Name of next node to visit "llm_call_1": "llm_call_1", "llm_call_1" : "llm_call_1" , "llm_call_2": "llm_call_2", "llm_call_2" : "llm_call_2" , "llm_call_3": "llm_call_3", "llm_call_3" : "llm_call_3" , }, }, ) ) router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_1", END) router_builder . add_edge ( "llm_call_1" , END ) router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_2", END) router_builder . add_edge ( "llm_call_2" , END ) router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_3", END) router_builder . add_edge ( "llm_call_3" , END ) # Compile workflow # Compile workflow router_workflow = router_builder.compile() router_workflow = router_builder . compile () # Show the workflow # Show the workflow display(Image(router_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( router_workflow . get_graph () . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke state = router_workflow.invoke({"input": "Write me a joke about cats"}) state = router_workflow . invoke ({ "input" : "Write me a joke about cats" }) print(state["output"]) print ( state [ "output" ]) from typing_extensions import Literal from typing_extensions import Literal from pydantic import BaseModel from pydantic import BaseModel from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage , SystemMessage # Schema for structured output to use as routing logic # Schema for structured output to use as routing logic class Route(BaseModel): class Route ( BaseModel ): step: Literal["poem", "story", "joke"] = Field( step : Literal [ "poem" , "story" , "joke" ] = Field ( None, description="The next step in the routing process" None , description = "The next step in the routing process" ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output router = llm.with_structured_output(Route) router = llm . with_structured_output ( Route ) @task @task def llm_call_1(input_: str): def llm_call_1 ( input_ : str ): """Write a story""" """Write a story""" result = llm.invoke(input_) result = llm . invoke ( input_ ) return result.content return result . content @task @task def llm_call_2(input_: str): def llm_call_2 ( input_ : str ): """Write a joke""" """Write a joke""" result = llm.invoke(input_) result = llm . invoke ( input_ ) return result.content return result . content @task @task def llm_call_3(input_: str): def llm_call_3 ( input_ : str ): """Write a poem""" """Write a poem""" result = llm.invoke(input_) result = llm . invoke ( input_ ) return result.content return result . content def llm_call_router(input_: str): def llm_call_router ( input_ : str ): """Route the input to the appropriate node""" """Route the input to the appropriate node""" # Run the augmented LLM with structured output to serve as routing logic # Run the augmented LLM with structured output to serve as routing logic decision = router.invoke( decision = router . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage( SystemMessage ( content="Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request." content = "Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request." ), ), HumanMessage(content=input_), HumanMessage ( content = input_ ), ] ] ) ) return decision.step return decision . step # Create workflow # Create workflow @entrypoint() @entrypoint () def router_workflow(input_: str): def router_workflow ( input_ : str ): next_step = llm_call_router(input_) next_step = llm_call_router ( input_ ) if next_step == "story": if next_step == "story" : llm_call = llm_call_1 llm_call = llm_call_1 elif next_step == "joke": elif next_step == "joke" : llm_call = llm_call_2 llm_call = llm_call_2 elif next_step == "poem": elif next_step == "poem" : llm_call = llm_call_3 llm_call = llm_call_3 return llm_call(input_).result() return llm_call ( input_ ) . result () # Invoke # Invoke for step in router_workflow.stream("Write me a joke about cats", stream_mode="updates"): for step in router_workflow . stream ( "Write me a joke about cats" , stream_mode = "updates" ): print(step) print ( step ) print("\n") print ( " \n " ) from typing import Annotated, List from typing import Annotated , List import operator import operator # Schema for structured output to use in planning # Schema for structured output to use in planning class Section(BaseModel): class Section ( BaseModel ): name: str = Field( name : str = Field ( description="Name for this section of the report.", description = "Name for this section of the report." , ) ) description: str = Field( description : str = Field ( description="Brief overview of the main topics and concepts to be covered in this section.", description = "Brief overview of the main topics and concepts to be covered in this section." , ) ) class Sections(BaseModel): class Sections ( BaseModel ): sections: List[Section] = Field( sections : List [ Section ] = Field ( description="Sections of the report.", description = "Sections of the report." , ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output planner = llm.with_structured_output(Sections) planner = llm . with_structured_output ( Sections ) from langgraph.constants import Send from langgraph.constants import Send # Graph state # Graph state class State(TypedDict): class State ( TypedDict ): topic: str # Report topic topic : str # Report topic sections: list[Section] # List of report sections sections : list [ Section ] # List of report sections completed_sections: Annotated[ completed_sections : Annotated [ list, operator.add list , operator . add ] # All workers write to this key in parallel ] # All workers write to this key in parallel final_report: str # Final report final_report : str # Final report # Worker state # Worker state class WorkerState(TypedDict): class WorkerState ( TypedDict ): section: Section section : Section completed_sections: Annotated[list, operator.add] completed_sections : Annotated [ list , operator . add ] # Nodes # Nodes def orchestrator(state: State): def orchestrator ( state : State ): """Orchestrator that generates a plan for the report""" """Orchestrator that generates a plan for the report""" # Generate queries # Generate queries report_sections = planner.invoke( report_sections = planner . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage(content="Generate a plan for the report."), SystemMessage ( content = "Generate a plan for the report." ), HumanMessage(content=f"Here is the report topic: {state['topic']}"), HumanMessage ( content = f "Here is the report topic: { state [ 'topic' ] } " ), ] ] ) ) return {"sections": report_sections.sections} return { "sections" : report_sections . sections } def llm_call(state: WorkerState): def llm_call ( state : WorkerState ): """Worker writes a section of the report""" """Worker writes a section of the report""" # Generate section # Generate section section = llm.invoke( section = llm . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage( SystemMessage ( content="Write a report section following the provided name and description. Include no preamble for each section. Use markdown formatting." content = "Write a report section following the provided name and description. Include no preamble for each section. Use markdown formatting." ), ), HumanMessage( HumanMessage ( content=f"Here is the section name: {state['section'].name} and description: {state['section'].description}" content = f "Here is the section name: { state [ 'section' ] . name } and description: { state [ 'section' ] . description } " ), ), ] ] ) ) # Write the updated section to completed sections # Write the updated section to completed sections return {"completed_sections": [section.content]} return { "completed_sections" : [ section . content ]} def synthesizer(state: State): def synthesizer ( state : State ): """Synthesize full report from sections""" """Synthesize full report from sections""" # List of completed sections # List of completed sections completed_sections = state["completed_sections"] completed_sections = state [ "completed_sections" ] # Format completed section to str to use as context for final sections # Format completed section to str to use as context for final sections completed_report_sections = "\n\n---\n\n".join(completed_sections) completed_report_sections = " \n\n --- \n\n " . join ( completed_sections ) return {"final_report": completed_report_sections} return { "final_report" : completed_report_sections } # Conditional edge function to create llm_call workers that each write a section of the report # Conditional edge function to create llm_call workers that each write a section of the report def assign_workers(state: State): def assign_workers ( state : State ): """Assign a worker to each section in the plan""" """Assign a worker to each section in the plan""" # Kick off section writing in parallel via Send() API # Kick off section writing in parallel via Send() API return [Send("llm_call", {"section": s}) for s in state["sections"]] return [ Send ( "llm_call" , { "section" : s }) for s in state [ "sections" ]] # Build workflow # Build workflow orchestrator_worker_builder = StateGraph(State) orchestrator_worker_builder = StateGraph ( State ) # Add the nodes # Add the nodes orchestrator_worker_builder.add_node("orchestrator", orchestrator) orchestrator_worker_builder . add_node ( "orchestrator" , orchestrator ) orchestrator_worker_builder.add_node("llm_call", llm_call) orchestrator_worker_builder . add_node ( "llm_call" , llm_call ) orchestrator_worker_builder.add_node("synthesizer", synthesizer) orchestrator_worker_builder . add_node ( "synthesizer" , synthesizer ) # Add edges to connect nodes # Add edges to connect nodes orchestrator_worker_builder.add_edge(START, "orchestrator") orchestrator_worker_builder . add_edge ( START , "orchestrator" ) orchestrator_worker_builder.add_conditional_edges( orchestrator_worker_builder . add_conditional_edges ( "orchestrator", assign_workers, ["llm_call"] "orchestrator" , assign_workers , [ "llm_call" ] ) ) orchestrator_worker_builder.add_edge("llm_call", "synthesizer") orchestrator_worker_builder . add_edge ( "llm_call" , "synthesizer" ) orchestrator_worker_builder.add_edge("synthesizer", END) orchestrator_worker_builder . add_edge ( "synthesizer" , END ) # Compile the workflow # Compile the workflow orchestrator_worker = orchestrator_worker_builder.compile() orchestrator_worker = orchestrator_worker_builder . compile () # Show the workflow # Show the workflow display(Image(orchestrator_worker.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( orchestrator_worker . get_graph () . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke state = orchestrator_worker.invoke({"topic": "Create a report on LLM scaling laws"}) state = orchestrator_worker . invoke ({ "topic" : "Create a report on LLM scaling laws" }) from IPython.display import Markdown from IPython.display import Markdown Markdown(state["final_report"]) Markdown ( state [ "final_report" ]) from typing import List from typing import List # Schema for structured output to use in planning # Schema for structured output to use in planning class Section(BaseModel): class Section ( BaseModel ): name: str = Field( name : str = Field ( description="Name for this section of the report.", description = "Name for this section of the report." , ) ) description: str = Field( description : str = Field ( description="Brief overview of the main topics and concepts to be covered in this section.", description = "Brief overview of the main topics and concepts to be covered in this section." , ) ) class Sections(BaseModel): class Sections ( BaseModel ): sections: List[Section] = Field( sections : List [ Section ] = Field ( description="Sections of the report.", description = "Sections of the report." , ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output planner = llm.with_structured_output(Sections) planner = llm . with_structured_output ( Sections ) @task @task def orchestrator(topic: str): def orchestrator ( topic : str ): """Orchestrator that generates a plan for the report""" """Orchestrator that generates a plan for the report""" # Generate queries # Generate queries report_sections = planner.invoke( report_sections = planner . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage(content="Generate a plan for the report."), SystemMessage ( content = "Generate a plan for the report." ), HumanMessage(content=f"Here is the report topic: {topic}"), HumanMessage ( content = f "Here is the report topic: { topic } " ), ] ] ) ) return report_sections.sections return report_sections . sections @task @task def llm_call(section: Section): def llm_call ( section : Section ): """Worker writes a section of the report""" """Worker writes a section of the report""" # Generate section # Generate section result = llm.invoke( result = llm . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage(content="Write a report section."), SystemMessage ( content = "Write a report section." ), HumanMessage( HumanMessage ( content=f"Here is the section name: {section.name} and description: {section.description}" content = f "Here is the section name: { section . name } and description: { section . description } " ), ), ] ] ) ) # Write the updated section to completed sections # Write the updated section to completed sections return result.content return result . content @task @task def synthesizer(completed_sections: list[str]): def synthesizer ( completed_sections : list [ str ]): """Synthesize full report from sections""" """Synthesize full report from sections""" final_report = "\n\n---\n\n".join(completed_sections) final_report = " \n\n --- \n\n " . join ( completed_sections ) return final_report return final_report @entrypoint() @entrypoint () def orchestrator_worker(topic: str): def orchestrator_worker ( topic : str ): sections = orchestrator(topic).result() sections = orchestrator ( topic ) . result () section_futures = [llm_call(section) for section in sections] section_futures = [ llm_call ( section ) for section in sections ] final_report = synthesizer( final_report = synthesizer ( [section_fut.result() for section_fut in section_futures] [ section_fut . result () for section_fut in section_futures ] ).result() ) . result () return final_report return final_report # Invoke # Invoke report = orchestrator_worker.invoke("Create a report on LLM scaling laws") report = orchestrator_worker . invoke ( "Create a report on LLM scaling laws" ) from IPython.display import Markdown from IPython.display import Markdown Markdown(report) Markdown ( report ) # Graph state # Graph state class State(TypedDict): class State ( TypedDict ): joke: str joke : str topic: str topic : str feedback: str feedback : str funny_or_not: str funny_or_not : str # Schema for structured output to use in evaluation # Schema for structured output to use in evaluation class Feedback(BaseModel): class Feedback ( BaseModel ): grade: Literal["funny", "not funny"] = Field( grade : Literal [ "funny" , "not funny" ] = Field ( description="Decide if the joke is funny or not.", description = "Decide if the joke is funny or not." , ) ) feedback: str = Field( feedback : str = Field ( description="If the joke is not funny, provide feedback on how to improve it.", description = "If the joke is not funny, provide feedback on how to improve it." , ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output evaluator = llm.with_structured_output(Feedback) evaluator = llm . with_structured_output ( Feedback ) # Nodes # Nodes def llm_call_generator(state: State): def llm_call_generator ( state : State ): """LLM generates a joke""" """LLM generates a joke""" if state.get("feedback"): if state . get ( "feedback" ): msg = llm.invoke( msg = llm . invoke ( f"Write a joke about {state['topic']} but take into account the feedback: {state['feedback']}" f "Write a joke about { state [ 'topic' ] } but take into account the feedback: { state [ 'feedback' ] } " ) ) else: else : msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {state['topic']}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a joke about { state [ 'topic' ] } " ) return {"joke": msg.content} return { "joke" : msg . content } def llm_call_evaluator(state: State): def llm_call_evaluator ( state : State ): """LLM evaluates the joke""" """LLM evaluates the joke""" grade = evaluator.invoke(f"Grade the joke {state['joke']}") grade = evaluator . invoke ( f "Grade the joke { state [ 'joke' ] } " ) return {"funny_or_not": grade.grade, "feedback": grade.feedback} return { "funny_or_not" : grade . grade , "feedback" : grade . feedback } # Conditional edge function to route back to joke generator or end based upon feedback from the evaluator # Conditional edge function to route back to joke generator or end based upon feedback from the evaluator def route_joke(state: State): def route_joke ( state : State ): """Route back to joke generator or end based upon feedback from the evaluator""" """Route back to joke generator or end based upon feedback from the evaluator""" if state["funny_or_not"] == "funny": if state [ "funny_or_not" ] == "funny" : return "Accepted" return "Accepted" elif state["funny_or_not"] == "not funny": elif state [ "funny_or_not" ] == "not funny" : return "Rejected + Feedback" return "Rejected + Feedback" # Build workflow # Build workflow optimizer_builder = StateGraph(State) optimizer_builder = StateGraph ( State ) # Add the nodes # Add the nodes optimizer_builder.add_node("llm_call_generator", llm_call_generator) optimizer_builder . add_node ( "llm_call_generator" , llm_call_generator ) optimizer_builder.add_node("llm_call_evaluator", llm_call_evaluator) optimizer_builder . add_node ( "llm_call_evaluator" , llm_call_evaluator ) # Add edges to connect nodes # Add edges to connect nodes optimizer_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call_generator") optimizer_builder . add_edge ( START , "llm_call_generator" ) optimizer_builder.add_edge("llm_call_generator", "llm_call_evaluator") optimizer_builder . add_edge ( "llm_call_generator" , "llm_call_evaluator" ) optimizer_builder.add_conditional_edges( optimizer_builder . add_conditional_edges ( "llm_call_evaluator", "llm_call_evaluator" , route_joke, route_joke , { # Name returned by route_joke : Name of next node to visit { # Name returned by route_joke : Name of next node to visit "Accepted": END, "Accepted" : END , "Rejected + Feedback": "llm_call_generator", "Rejected + Feedback" : "llm_call_generator" , }, }, ) ) # Compile the workflow # Compile the workflow optimizer_workflow = optimizer_builder.compile() optimizer_workflow = optimizer_builder . compile () # Show the workflow # Show the workflow display(Image(optimizer_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( optimizer_workflow . get_graph () . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke state = optimizer_workflow.invoke({"topic": "Cats"}) state = optimizer_workflow . invoke ({ "topic" : "Cats" }) print(state["joke"]) print ( state [ "joke" ]) # Schema for structured output to use in evaluation # Schema for structured output to use in evaluation class Feedback(BaseModel): class Feedback ( BaseModel ): grade: Literal["funny", "not funny"] = Field( grade : Literal [ "funny" , "not funny" ] = Field ( description="Decide if the joke is funny or not.", description = "Decide if the joke is funny or not." , ) ) feedback: str = Field( feedback : str = Field ( description="If the joke is not funny, provide feedback on how to improve it.", description = "If the joke is not funny, provide feedback on how to improve it." , ) ) # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output # Augment the LLM with schema for structured output evaluator = llm.with_structured_output(Feedback) evaluator = llm . with_structured_output ( Feedback ) # Nodes # Nodes @task @task def llm_call_generator(topic: str, feedback: Feedback): def llm_call_generator ( topic : str , feedback : Feedback ): """LLM generates a joke""" """LLM generates a joke""" if feedback: if feedback : msg = llm.invoke( msg = llm . invoke ( f"Write a joke about {topic} but take into account the feedback: {feedback}" f "Write a joke about { topic } but take into account the feedback: { feedback } " ) ) else: else : msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {topic}") msg = llm . invoke ( f "Write a joke about { topic } " ) return msg.content return msg . content @task @task def llm_call_evaluator(joke: str): def llm_call_evaluator ( joke : str ): """LLM evaluates the joke""" """LLM evaluates the joke""" feedback = evaluator.invoke(f"Grade the joke {joke}") feedback = evaluator . invoke ( f "Grade the joke { joke } " ) return feedback return feedback @entrypoint() @entrypoint () def optimizer_workflow(topic: str): def optimizer_workflow ( topic : str ): feedback = None feedback = None while True: while True : joke = llm_call_generator(topic, feedback).result() joke = llm_call_generator ( topic , feedback ) . result () feedback = llm_call_evaluator(joke).result() feedback = llm_call_evaluator ( joke ) . result () if feedback.grade == "funny": if feedback . grade == "funny" : break break return joke return joke # Invoke # Invoke for step in optimizer_workflow.stream("Cats", stream_mode="updates"): for step in optimizer_workflow . stream ( "Cats" , stream_mode = "updates" ): print(step) print ( step ) print("\n") print ( " \n " ) from langchain_core.tools import tool from langchain_core.tools import tool # Define tools # Define tools @tool @tool def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int: def multiply ( a : int , b : int ) -> int : """Multiply a and b. """Multiply a and b. Args: Args: a: first int a: first int b: second int b: second int """ """ return a * b return a * b @tool @tool def add(a: int, b: int) -> int: def add ( a : int , b : int ) -> int : """Adds a and b. """Adds a and b. Args: Args: a: first int a: first int b: second int b: second int """ """ return a + b return a + b @tool @tool def divide(a: int, b: int) -> float: def divide ( a : int , b : int ) -> float : """Divide a and b. """Divide a and b. Args: Args: a: first int a: first int b: second int b: second int """ """ return a / b return a / b # Augment the LLM with tools # Augment the LLM with tools tools = [add, multiply, divide] tools = [ add , multiply , divide ] tools_by_name = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools} tools_by_name = { tool . name : tool for tool in tools } llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools) llm_with_tools = llm . bind_tools ( tools ) from langgraph.graph import MessagesState from langgraph.graph import MessagesState from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage, ToolMessage from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage , HumanMessage , ToolMessage # Nodes # Nodes def llm_call(state: MessagesState): def llm_call ( state : MessagesState ): """LLM decides whether to call a tool or not""" """LLM decides whether to call a tool or not""" return { return { "messages": [ "messages" : [ llm_with_tools.invoke( llm_with_tools . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage( SystemMessage ( content="You are a helpful assistant tasked with performing arithmetic on a set of inputs." content = "You are a helpful assistant tasked with performing arithmetic on a set of inputs." ) ) ] ] + state["messages"] + state [ "messages" ] ) ) ] ] } } def tool_node(state: dict): def tool_node ( state : dict ): """Performs the tool call""" """Performs the tool call""" result = [] result = [] for tool_call in state["messages"][-1].tool_calls: for tool_call in state [ "messages" ][ - 1 ] . tool_calls : tool = tools_by_name[tool_call["name"]] tool = tools_by_name [ tool_call [ "name" ]] observation = tool.invoke(tool_call["args"]) observation = tool . invoke ( tool_call [ "args" ]) result.append(ToolMessage(content=observation, tool_call_id=tool_call["id"])) result . append ( ToolMessage ( content = observation , tool_call_id = tool_call [ "id" ])) return {"messages": result} return { "messages" : result } # Conditional edge function to route to the tool node or end based upon whether the LLM made a tool call # Conditional edge function to route to the tool node or end based upon whether the LLM made a tool call def should_continue(state: MessagesState) -> Literal["environment", END]: def should_continue ( state : MessagesState ) -> Literal [ "environment" , END ]: """Decide if we should continue the loop or stop based upon whether the LLM made a tool call""" """Decide if we should continue the loop or stop based upon whether the LLM made a tool call""" messages = state["messages"] messages = state [ "messages" ] last_message = messages[-1] last_message = messages [ - 1 ] # If the LLM makes a tool call, then perform an action # If the LLM makes a tool call, then perform an action if last_message.tool_calls: if last_message . tool_calls : return "Action" return "Action" # Otherwise, we stop (reply to the user) # Otherwise, we stop (reply to the user) return END return END # Build workflow # Build workflow agent_builder = StateGraph(MessagesState) agent_builder = StateGraph ( MessagesState ) # Add nodes # Add nodes agent_builder.add_node("llm_call", llm_call) agent_builder . add_node ( "llm_call" , llm_call ) agent_builder.add_node("environment", tool_node) agent_builder . add_node ( "environment" , tool_node ) # Add edges to connect nodes # Add edges to connect nodes agent_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call") agent_builder . add_edge ( START , "llm_call" ) agent_builder.add_conditional_edges( agent_builder . add_conditional_edges ( "llm_call", "llm_call" , should_continue, should_continue , { { # Name returned by should_continue : Name of next node to visit # Name returned by should_continue : Name of next node to visit "Action": "environment", "Action" : "environment" , END: END, END : END , }, }, ) ) agent_builder.add_edge("environment", "llm_call") agent_builder . add_edge ( "environment" , "llm_call" ) # Compile the agent # Compile the agent agent = agent_builder.compile() agent = agent_builder . compile () # Show the agent # Show the agent display(Image(agent.get_graph(xray=True).draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( agent . get_graph ( xray = True ) . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke messages = [HumanMessage(content="Add 3 and 4.")] messages = [ HumanMessage ( content = "Add 3 and 4." )] messages = agent.invoke({"messages": messages}) messages = agent . invoke ({ "messages" : messages }) for m in messages["messages"]: for m in messages [ "messages" ]: m.pretty_print() m . pretty_print () from langgraph.graph import add_messages from langgraph.graph import add_messages from langchain_core.messages import ( from langchain_core.messages import ( SystemMessage, SystemMessage , HumanMessage, HumanMessage , BaseMessage, BaseMessage , ToolCall, ToolCall , ) ) @task @task def call_llm(messages: list[BaseMessage]): def call_llm ( messages : list [ BaseMessage ]): """LLM decides whether to call a tool or not""" """LLM decides whether to call a tool or not""" return llm_with_tools.invoke( return llm_with_tools . invoke ( [ [ SystemMessage( SystemMessage ( content="You are a helpful assistant tasked with performing arithmetic on a set of inputs." content = "You are a helpful assistant tasked with performing arithmetic on a set of inputs." ) ) ] ] + messages + messages ) ) @task @task def call_tool(tool_call: ToolCall): def call_tool ( tool_call : ToolCall ): """Performs the tool call""" """Performs the tool call""" tool = tools_by_name[tool_call["name"]] tool = tools_by_name [ tool_call [ "name" ]] return tool.invoke(tool_call) return tool . invoke ( tool_call ) @entrypoint() @entrypoint () def agent(messages: list[BaseMessage]): def agent ( messages : list [ BaseMessage ]): llm_response = call_llm(messages).result() llm_response = call_llm ( messages ) . result () while True: while True : if not llm_response.tool_calls: if not llm_response . tool_calls : break break # Execute tools # Execute tools tool_result_futures = [ tool_result_futures = [ call_tool(tool_call) for tool_call in llm_response.tool_calls call_tool ( tool_call ) for tool_call in llm_response . tool_calls ] ] tool_results = [fut.result() for fut in tool_result_futures] tool_results = [ fut . result () for fut in tool_result_futures ] messages = add_messages(messages, [llm_response, *tool_results]) messages = add_messages ( messages , [ llm_response , * tool_results ]) llm_response = call_llm(messages).result() llm_response = call_llm ( messages ) . result () messages = add_messages(messages, llm_response) messages = add_messages ( messages , llm_response ) return messages return messages # Invoke # Invoke messages = [HumanMessage(content="Add 3 and 4.")] messages = [ HumanMessage ( content = "Add 3 and 4." )] for chunk in agent.stream(messages, stream_mode="updates"): for chunk in agent . stream ( messages , stream_mode = "updates" ): print(chunk) print ( chunk ) print("\n") print ( " \n " ) from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent # Pass in: # Pass in: # (1) the augmented LLM with tools # (1) the augmented LLM with tools # (2) the tools list (which is used to create the tool node) # (2) the tools list (which is used to create the tool node) pre_built_agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools=tools) pre_built_agent = create_react_agent ( llm , tools = tools ) # Show the agent # Show the agent display(Image(pre_built_agent.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) display ( Image ( pre_built_agent . get_graph () . draw_mermaid_png ())) # Invoke # Invoke messages = [HumanMessage(content="Add 3 and 4.")] messages = [ HumanMessage ( content = "Add 3 and 4." )] messages = pre_built_agent.invoke({"messages": messages}) messages = pre_built_agent . invoke ({ "messages" : messages }) for m in messages["messages"]: for m in messages [ "messages" ]: m.pretty_print() m . pretty_print () Previous Next This guide reviews common patterns for agentic systems. In describing these systems, it can be useful to make a distinction between "workflows" and "agents". One way to think about this difference is nicely explained here by Anthropic: Workflows are systems where LLMs and tools are orchestrated through predefined code paths.Agents, on the other hand, are systems where LLMs dynamically direct their own processes and tool usage, maintaining control over how they accomplish tasks. Here is a simple way to visualize these differences: When building agents and workflows, LangGraph offers a number of benefits including persistence, streaming, and support for debugging as well as deployment. You can use any chat model that supports structured outputs and tool calling. Below, we show the process of installing the packages, setting API keys, and testing structured outputs / tool calling for Anthropic. Initialize an LLM API Reference: ChatAnthropic LLM have augmentations that support building workflows and agents. These include structured outputs and tool calling, as shown in this image from the Anthropic blog: In prompt chaining, each LLM call processes the output of the previous one. As noted in the Anthropic blog: Prompt chaining decomposes a task into a sequence of steps, where each LLM call processes the output of the previous one. You can add programmatic checks (see "gate” in the diagram below) on any intermediate steps to ensure that the process is still on track. When to use this workflow: This workflow is ideal for situations where the task can be easily and cleanly decomposed into fixed subtasks. The main goal is to trade off latency for higher accuracy, by making each LLM call an easier task. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/a0281fca-3a71-46de-beee-791468607b75/r Resources: LangChain Academy See our lesson on Prompt Chaining here. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/332fa4fc-b6ca-416e-baa3-161625e69163/r With parallelization, LLMs work simultaneously on a task: LLMs can sometimes work simultaneously on a task and have their outputs aggregated programmatically. This workflow, parallelization, manifests in two key variations: Sectioning: Breaking a task into independent subtasks run in parallel. Voting: Running the same task multiple times to get diverse outputs. When to use this workflow: Parallelization is effective when the divided subtasks can be parallelized for speed, or when multiple perspectives or attempts are needed for higher confidence results. For complex tasks with multiple considerations, LLMs generally perform better when each consideration is handled by a separate LLM call, allowing focused attention on each specific aspect. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/3be2e53c-ca94-40dd-934f-82ff87fac277/r Resources: Documentation See our documentation on parallelization here. LangChain Academy See our lesson on parallelization here. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/623d033f-e814-41e9-80b1-75e6abb67801/r Routing classifies an input and directs it to a followup task. As noted in the Anthropic blog: Routing classifies an input and directs it to a specialized followup task. This workflow allows for separation of concerns, and building more specialized prompts. Without this workflow, optimizing for one kind of input can hurt performance on other inputs. When to use this workflow: Routing works well for complex tasks where there are distinct categories that are better handled separately, and where classification can be handled accurately, either by an LLM or a more traditional classification model/algorithm. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/c4580b74-fe91-47e4-96fe-7fac598d509c/r Resources: LangChain Academy See our lesson on routing here. Examples Here is RAG workflow that routes questions. See our video here. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/5e2eb979-82dd-402c-b1a0-a8cceaf2a28a/r With orchestrator-worker, an orchestrator breaks down a task and delegates each sub-task to workers. As noted in the Anthropic blog: In the orchestrator-workers workflow, a central LLM dynamically breaks down tasks, delegates them to worker LLMs, and synthesizes their results. When to use this workflow: This workflow is well-suited for complex tasks where you can’t predict the subtasks needed (in coding, for example, the number of files that need to be changed and the nature of the change in each file likely depend on the task). Whereas it’s topographically similar, the key difference from parallelization is its flexibility—subtasks aren't pre-defined, but determined by the orchestrator based on the specific input. Creating Workers in LangGraph Because orchestrator-worker workflows are common, LangGraph has the Send API to support this. It lets you dynamically create worker nodes and send each one a specific input. Each worker has its own state, and all worker outputs are written to a shared state key that is accessible to the orchestrator graph. This gives the orchestrator access to all worker output and allows it to synthesize them into a final output. As you can see below, we iterate over a list of sections and Send each to a worker node. See further documentation here and here. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/78cbcfc3-38bf-471d-b62a-b299b144237d/r Resources: LangChain Academy See our lesson on orchestrator-worker here. Examples Here is a project that uses orchestrator-worker for report planning and writing. See our video here. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/75a636d0-6179-4a12-9836-e0aa571e87c5/r In the evaluator-optimizer workflow, one LLM call generates a response while another provides evaluation and feedback in a loop: In the evaluator-optimizer workflow, one LLM call generates a response while another provides evaluation and feedback in a loop. When to use this workflow: This workflow is particularly effective when we have clear evaluation criteria, and when iterative refinement provides measurable value. The two signs of good fit are, first, that LLM responses can be demonstrably improved when a human articulates their feedback; and second, that the LLM can provide such feedback. This is analogous to the iterative writing process a human writer might go through when producing a polished document. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/86ab3e60-2000-4bff-b988-9b89a3269789/r Resources: Examples Here is an assistant that uses evaluator-optimizer to improve a report. See our video here. Here is a RAG workflow that grades answers for hallucinations or errors. See our video here. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/f66830be-4339-4a6b-8a93-389ce5ae27b4/r Agents are typically implemented as an LLM performing actions (via tool-calling) based on environmental feedback in a loop. As noted in the Anthropic blog: Agents can handle sophisticated tasks, but their implementation is often straightforward. They are typically just LLMs using tools based on environmental feedback in a loop. It is therefore crucial to design toolsets and their documentation clearly and thoughtfully. When to use agents: Agents can be used for open-ended problems where it’s difficult or impossible to predict the required number of steps, and where you can’t hardcode a fixed path. The LLM will potentially operate for many turns, and you must have some level of trust in its decision-making. Agents' autonomy makes them ideal for scaling tasks in trusted environments. API Reference: tool LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/051f0391-6761-4f8c-a53b-22231b016690/r Resources: LangChain Academy See our lesson on agents here. Examples Here is a project that uses a tool calling agent to create / store long-term memories. LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/42ae8bf9-3935-4504-a081-8ddbcbfc8b2e/r LangGraph also provides a pre-built method for creating an agent as defined above (using the create_react_agent function): https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/how-tos/create-react-agent/ API Reference: create_react_agent LangSmith Trace https://smith.langchain.com/public/abab6a44-29f6-4b97-8164-af77413e494d/r By constructing each of the above in LangGraph, we get a few things: LangGraph persistence layer supports interruption and approval of actions (e.g., Human In The Loop). See Module 3 of LangChain Academy. LangGraph persistence layer supports conversational (short-term) memory and long-term memory. See Modules 2 and 5 of LangChain Academy: LangGraph provides several ways to stream workflow / agent outputs or intermediate state. See Module 3 of LangChain Academy. LangGraph provides an easy on-ramp for deployment, observability, and evaluation. See module 6 of LangChain Academy. We use cookies to recognize your repeated visits and preferences, as well as to measure the effectiveness of our documentation and whether users find what they're searching for. Clicking "Accept" makes our documentation better. Thank you! ❤️